Tesla recently began rolling out a simplified version of its Full Self-Driving (Tesla FSD v13.2) to select early-access customers. While this release marks some progress, it also reflects challenges in Tesla’s ambitious timeline to achieve unsupervised self-driving by the end of Q2 2025. Here’s a breakdown of the current release, its features, challenges, and what lies ahead for Tesla’s autonomous driving journey.

What’s New in FSD v13.2?
Tesla’s FSD v13.2 comes with several enhancements, aiming to improve the overall driving experience. Below are the highlights of the release:
Key Features in v13.2:
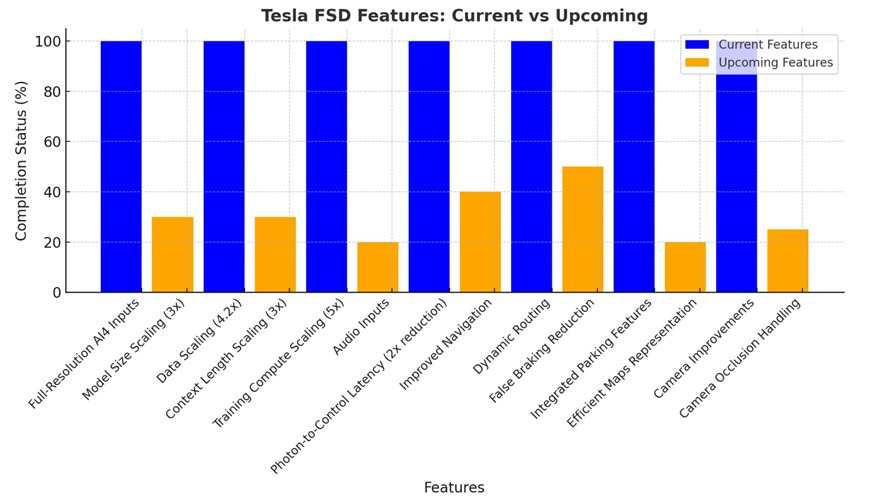
- 36 Hz Full-Resolution AI4 Video Inputs: Enhances the system’s ability to process road scenarios with greater clarity.
- Native AI4 Neural Networks: Improved architecture for more efficient decision-making.
- Data and Compute Scaling:
- 4.2x Data Scaling: Improves learning capabilities by using more extensive datasets.
- 5x Training Compute Scaling: Enabled by Tesla’s Cortext cluster, this accelerates neural network training.
- Photon-to-Control Latency Halved: Reduces delays in processing real-time information.
- Dynamic Routing: Better rerouting capabilities around road closures detected by the fleet.
- Integrated Parking Features: Allows supervised activation of FSD from Park and includes unpark, reverse, and park functionalities.
- Smoother Navigation: Redesigned controllers for more accurate movement tracking.
- Camera Improvements: Enhanced cleaning processes and better predictions to avoid collisions.
What’s Missing?
While the rollout introduces significant advancements, it’s not the full v13 version originally promised for November. Several critical features remain in development and are listed as “upcoming improvements”:
Planned Enhancements:
- 3x Model Size and Context Length Scaling: Critical for improving decision-making in complex scenarios.
- Audio Inputs: Helps detect emergency vehicles and adapt accordingly.
- Navigation Improvements: Features like parking in garages or driveways.
- Camera Occlusion Handling: Reduces blind spots from obstructed camera views.
- False Braking Reduction: Aimed at smoother driving in parking lots.
These “upcoming improvements” were initially promised as part of the v13 release, leaving some owners disappointed.

Tesla’s Self-Driving Challenges
Missed Deadlines
Tesla’s goal of achieving unsupervised self-driving by mid-2025 has been viewed as overly optimistic. The company’s struggle to meet even short-term goals, like delivering a complete version of FSD v13 by November 2023, raises concerns about its ability to stick to its timeline.
For context, Tesla had initially targeted October for the v13 release, only to delay it to November. Even now, only Hardware 4 (HW4) users are receiving a limited version of the update.
Miles Between Disengagement
One key metric in autonomous driving is miles between disengagement—how far the system can operate without human intervention. While v13 introduces features like unpark, reverse, and park, these are just stepping stones. To achieve unsupervised self-driving, Tesla must increase miles between disengagement by 2,000x within a remarkably short period—an enormous challenge.
FSD v12 vs. FSD v13.2
| Feature | FSD v12 | FSD v13.2 |
|---|---|---|
| Video Input Resolution | Lower resolution | Full-resolution AI4, 36 Hz inputs |
| Data Scaling | Standard | 4.2x scaling |
| Training Compute | Limited | 5x scaling with Cortext cluster |
| Navigation Enhancements | Basic rerouting | Dynamic rerouting for road closures |
| Parking Features | Standard supervised parking | Integrated unpark, reverse, and park |
| Photon-to-Control Latency | Standard | Reduced by 50% |
| Upcoming Improvements | None | Audio inputs, improved occlusion handling |
Where Tesla Stands Today
The Positives
- Improved Features: Tesla’s advancements in compute power and data scaling reflect significant progress.
- Enhanced Parking Capabilities: The ability to unpark, reverse, and park autonomously adds convenience and usability.
- Dynamic Routing: The fleet’s ability to detect and reroute around road closures demonstrates improved adaptability.
The Concerns
- Timeline Doubts: The continual delays raise skepticism about Tesla’s ability to meet its 2025 goal for unsupervised driving.
- Incremental Progress: While v13.2 offers improvements, achieving full autonomy requires exponential leaps, not incremental changes.
- Customer Frustration: Repeated delays and partial updates are testing the patience of Tesla owners who expected more robust features.
What’s Next for Tesla?
The road to unsupervised self-driving remains steep, with significant hurdles ahead. To stay competitive and maintain trust, Tesla must focus on:
- Delivering Promised Features: Meeting deadlines for upcoming enhancements like 3x model scaling and audio inputs.
- Transparency: Clear communication with customers about realistic timelines and capabilities.
- Scaling Miles Between Disengagement: Making rapid advancements to improve reliability and safety.
Final Thoughts
Tesla’s FSD v13.2 represents a step forward but highlights the challenges of autonomous driving development. While the update introduces meaningful improvements, it falls short of the ambitious promises set earlier this year.
The company’s journey toward unsupervised self-driving will require not only technological breakthroughs but also better alignment between promises and delivery. As Tesla continues to push boundaries, the question remains: can it balance innovation with the reliability and trust its customers demand?
The coming months will be critical for Tesla as it works to meet its ambitious goals and redefine the future of autonomous driving.
PEOPLE WHO READ THIS, ALSO READ




